Download Hyperledger Fabric Certified Practitioner.HFCP.Pass4Success.2026-01-25.32q.tqb
| Vendor: | Linux Foundation |
| Exam Code: | HFCP |
| Exam Name: | Hyperledger Fabric Certified Practitioner |
| Date: | Jan 25, 2026 |
| File Size: | 114 KB |
How to open TQB files?
Files with TQB (Taurus Question Bank) extension can be opened by Taurus Exam Studio.
Purchase
Coupon: TAURUSSIM_20OFF
Discount: 20%
Demo Questions
Question 1
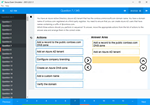
In Hyperledger Fabric, what is used if end users of the application want to keep their private key secret?
- Offline signing
- Online signing
- No signing is required
- Shared signing
Correct answer: A
Explanation:
In Hyperledger Fabric, if end users of the application want to keep their private key secret and secure, they would use offline signing. Offline signing involves signing transactions on a device or in an environment that is not connected to the network or the internet. This method ensures that the private key used for signing does not get exposed to the network and reduces the risk of compromise. Offline signing is especially important in scenarios where security and privacy are paramount, as it allows users to maintain control over their private keys at all times. In Hyperledger Fabric, if end users of the application want to keep their private key secret and secure, they would use offline signing. Offline signing involves signing transactions on a device or in an environment that is not connected to the network or the internet. This method ensures that the private key used for signing does not get exposed to the network and reduces the risk of compromise. Offline signing is especially important in scenarios where security and privacy are paramount, as it allows users to maintain control over their private keys at all times.
Question 2
An enterprise blockchain is a permission blockchain node distributed to whom?
- Administration data center
- Nodes distributed with a validator
- Member organizations
- Nodes distributed on a public Blockchain
Correct answer: C
Explanation:
In Hyperledger Fabric, the enterprise blockchain is a permissioned network where nodes are distributed among the member organizations that participate in the blockchain network. This is in contrast to a public blockchain where anyone can participate anonymously. In a permissioned blockchain like Hyperledger Fabric, the participants are known entities within a business network, such as enterprises or organizations, that have specific permissions and roles within the network. This setup enhances security and trust as each participant is vetted and authorized to take part in the network operations. The architecture of Hyperledger Fabric is designed to support such a governance model, where multiple organizations can interact in a secure and regulated environment, maintaining their own ledgers but sharing data that require consensus across known entities. In Hyperledger Fabric, the enterprise blockchain is a permissioned network where nodes are distributed among the member organizations that participate in the blockchain network. This is in contrast to a public blockchain where anyone can participate anonymously. In a permissioned blockchain like Hyperledger Fabric, the participants are known entities within a business network, such as enterprises or organizations, that have specific permissions and roles within the network. This setup enhances security and trust as each participant is vetted and authorized to take part in the network operations. The architecture of Hyperledger Fabric is designed to support such a governance model, where multiple organizations can interact in a secure and regulated environment, maintaining their own ledgers but sharing data that require consensus across known entities.
Question 3
Which of the following statements describes Chaincode correctly?
- Chaincode is software for creating new blocks on the ledger.
- Chaincode is software defining assets and transaction instructions for modifying the assets on the ledger.
- Chaincode is a legally enforceable business contract between organizations.
- Chaincode is a code of conduct to manage a blockchain consortium.
Correct answer: B
Explanation:
Chaincode in Hyperledger Fabric is essentially smart contract software that defines assets and the transaction instructions for modifying these assets on the ledger. Chaincode functions as the business logic layer of the network, where the rules for interacting with the ledger are specified. It is executed on the network peers and is used to encode the policies and constraints associated with asset exchanges or updates within the business network. This setup allows organizations to automate processes and enforce consistency and compliance across transactions. Chaincode in Hyperledger Fabric is essentially smart contract software that defines assets and the transaction instructions for modifying these assets on the ledger. Chaincode functions as the business logic layer of the network, where the rules for interacting with the ledger are specified. It is executed on the network peers and is used to encode the policies and constraints associated with asset exchanges or updates within the business network. This setup allows organizations to automate processes and enforce consistency and compliance across transactions.
Question 4
After the transaction that contains the delState("A") function is committed, what happens to the ledger and state database?
- getstate('A') function returns the current state of the key 'A'.
- The deleting transaction sets an empty value to the key 'A' in the write set.
- The state of the key 'A' is removed from the state database, but its history remains in the ledger.
- All transaction histories which updated the state 'A' are deleted from the ledger.
Correct answer: C
Explanation:
In Hyperledger Fabric, when a transaction that includes the delState('A') function is committed, it results in the removal of the state of the key 'A' from the current state database. However, the history of all transactions that have affected the key 'A' remains intact in the ledger. This operation ensures that while the current state reflects the deletion, the immutability and traceability of the ledger are preserved, allowing for auditability and verification of past states. Options such as setting an empty value to the key or altering the transaction history are not supported, as they would violate the principles of immutability and transparency central to blockchain technology. Therefore, the correct outcome of a delState('A') operation is that the current state of 'A' is deleted, but its transaction history remains accessible in the ledger. In Hyperledger Fabric, when a transaction that includes the delState('A') function is committed, it results in the removal of the state of the key 'A' from the current state database. However, the history of all transactions that have affected the key 'A' remains intact in the ledger. This operation ensures that while the current state reflects the deletion, the immutability and traceability of the ledger are preserved, allowing for auditability and verification of past states. Options such as setting an empty value to the key or altering the transaction history are not supported, as they would violate the principles of immutability and transparency central to blockchain technology. Therefore, the correct outcome of a delState('A') operation is that the current state of 'A' is deleted, but its transaction history remains accessible in the ledger.
Question 5
Which subcommand adds a peer to a channel in Hyperledger Fabric?
- peer channel fetch
- peer channel creace
- peer channel updace
- peer channel join
Correct answer: D
Explanation:
In Hyperledger Fabric, the correct subcommand to add a peer to a channel is peer channel join. This command is used by a peer node to join an existing channel. The command requires a block to be specified which typically is the genesis block of the channel, allowing the peer to synchronize with the channel's ledger from the beginning. Other commands like peer channel fetch, peer channel create, and peer channel update serve different purposes. peer channel fetch retrieves blocks from a channel, peer channel create is used to set up a new channel, and peer channel update modifies channel settings. Thus, peer channel join is the specific command used to connect a peer to a channel. In Hyperledger Fabric, the correct subcommand to add a peer to a channel is peer channel join. This command is used by a peer node to join an existing channel. The command requires a block to be specified which typically is the genesis block of the channel, allowing the peer to synchronize with the channel's ledger from the beginning. Other commands like peer channel fetch, peer channel create, and peer channel update serve different purposes. peer channel fetch retrieves blocks from a channel, peer channel create is used to set up a new channel, and peer channel update modifies channel settings. Thus, peer channel join is the specific command used to connect a peer to a channel.
Question 6
Which of the following is the identity solution in Hyperledger Fabric?
- Hyperledger Fabric Orderer
- Hyperledger Fabric CA
- Hyperledger Fabric SDK
- Membership Service Providers
Correct answer: D
Explanation:
In Hyperledger Fabric, the identity solution that manages user identities and authenticates participants on the network is facilitated by Membership Service Providers (MSPs). MSPs are crucial for defining the rules by which identities are validated, authenticated, and allowed access to the network. MSPs handle the issuance of certificates and define the roles and permissions associated with participant identities, enabling permissioned interactions on the blockchain. This differs from Hyperledger Fabric CA, which primarily issues and revokes certificates as part of identity management but is used in conjunction with MSPs to provide comprehensive identity solutions within the network. In Hyperledger Fabric, the identity solution that manages user identities and authenticates participants on the network is facilitated by Membership Service Providers (MSPs). MSPs are crucial for defining the rules by which identities are validated, authenticated, and allowed access to the network. MSPs handle the issuance of certificates and define the roles and permissions associated with participant identities, enabling permissioned interactions on the blockchain. This differs from Hyperledger Fabric CA, which primarily issues and revokes certificates as part of identity management but is used in conjunction with MSPs to provide comprehensive identity solutions within the network.
Question 7
What is true about the historic states in Hyperledger Fabric model?
- They can be modified by anyone with write access.
- Administrator role is required for access.
- They are immutable.
- They cannot be accessed by anyone.
Correct answer: C
Explanation:
In Hyperledger Fabric, the standard possibilities to configure parameters of a component, such as a peer or orderer, include using YAML configuration files, environment variables, and command-line interface (CLI) flags. This approach provides flexibility and allows for detailed control over the parameters that govern the behavior of these components . In Hyperledger Fabric, the standard possibilities to configure parameters of a component, such as a peer or orderer, include using YAML configuration files, environment variables, and command-line interface (CLI) flags. This approach provides flexibility and allows for detailed control over the parameters that govern the behavior of these components .
Question 8
What is the advantage of using state-based endorsement policy over a chaincode or collection level endorsement policy?
- It provides a way to set endorsement policy on a global Hyperledger Fabric farm level with one configuration
- It can be used without complex configuration transactions, only a JSON configuration file is needed.
- It provides fine-tuned endorsement policy on key level, update is possible without chaincode update
- It provides a way to set endorsement policy for multiply keys with one chaincode configuration update.
Correct answer: A
Explanation:
In Hyperledger Fabric, a range query with a start and end key is a type of query that searches for all ledger entries whose keys fall within the specified range defined by the startKey and endKey. This is used, for example, to retrieve a subset of assets from the ledger based on their key values, effectively iterating over a specified range . In Hyperledger Fabric, a range query with a start and end key is a type of query that searches for all ledger entries whose keys fall within the specified range defined by the startKey and endKey. This is used, for example, to retrieve a subset of assets from the ledger based on their key values, effectively iterating over a specified range .
Question 9
What is the purpose of the ordering service in Hyperledger Fabric model?
- To endorse transactions and update the world state.
- To manage the identities of the participants in the network
- To assemble transactions into blocks for the blockchain ledqer.
- To validate transactions and maintain the blockchain ledqer
Correct answer: D
Explanation:
In Hyperledger Fabric, if a user submits a transaction with no matching function specified in the smart contract, the unknownTransaction function is invoked by default. This function serves as a catch-all method that can be used to handle cases where the transaction type is not recognized, providing a mechanism to manage or log these occurrences effectively . In Hyperledger Fabric, if a user submits a transaction with no matching function specified in the smart contract, the unknownTransaction function is invoked by default. This function serves as a catch-all method that can be used to handle cases where the transaction type is not recognized, providing a mechanism to manage or log these occurrences effectively .
Question 10
What Fabric Gateway client API call could a client application use to update ledger state?
- Evaluate
- Invoke
- Update
- Submit
Correct answer: A
Explanation:
In Hyperledger Fabric, a range query with a start and end key is a type of query that searches for all ledger entries whose keys fall within the specified range defined by the startKey and endKey. This is used, for example, to retrieve a subset of assets from the ledger based on their key values, effectively iterating over a specified range . In Hyperledger Fabric, a range query with a start and end key is a type of query that searches for all ledger entries whose keys fall within the specified range defined by the startKey and endKey. This is used, for example, to retrieve a subset of assets from the ledger based on their key values, effectively iterating over a specified range .
HOW TO OPEN VCE FILES
Use VCE Exam Simulator to open VCE files

HOW TO OPEN VCEX FILES
Use ProfExam Simulator to open VCEX files


ProfExam at a 20% markdown
You have the opportunity to purchase ProfExam at a 20% reduced price
Get Now!